Introduction to Breakout Technique
Breakout methods are primarily based on the precept that value usually accelerates as soon as it strikes past an outlined vary of help/resistance or excessive/low. These breakout factors usually characterize a shift in market sentiment and are sometimes accompanied by elevated quantity and volatility.
In sensible phrases, a breakout happens when value closes above a resistance stage or beneath a help stage that has been holding for a time frame. Merchants use these moments to enter the market, aiming to capitalize on the momentum that always follows such a transfer. Breakouts can provoke new developments, making them priceless entry factors for each short-term and long-term merchants.
Recognition of Breakout Technique
Breakout buying and selling is likely one of the most generally adopted methods amongst skilled and retail merchants for a number of causes:
Clear Entry and Exit RulesBreakout methods depend on predefined value ranges, lowering ambiguity in buying and selling choices. Momentum AlignmentTrades are aligned with directional momentum, growing the likelihood of follow-through. Applicability Throughout MarketsEffective in foreign exchange, commodities, indices, and even crypto, breakout rules are market-agnostic. Efficient Throughout Volatility SpikesNews releases, session openings, and macroeconomic occasions usually set off breakouts, making the technique efficient throughout key time home windows.
Its mixture of simplicity and statistical edge makes it a cornerstone of many buying and selling programs and Skilled Advisors.
Benefit of Utilizing a Breakout Technique EA
Utilizing an Skilled Advisor (EA) to automate breakout buying and selling introduces a number of efficiency and comfort advantages:
Velocity and PrecisionThe EA locations and manages orders at exact ranges and instances with out human delay. Eliminates Human EmotionThe system executes trades primarily based purely on logic and guidelines, avoiding emotional errors. Time-Primarily based ManagementThis EA consists of options like time-to-cancel for untriggered orders and time-based profit-taking, enhancing management. Field Sizing and Dynamic SLThe cease loss is intelligently primarily based on the dimensions of the breakout field, adapting to market circumstances. Trailing Cease IntegrationUsers can allow or disable trailing cease options for locking in earnings after breakout. Twin Mode: RBO and OBOSupports each range-based and session-opening breakouts with full flexibility.
This permits for environment friendly, disciplined, and around-the-clock operation with out the necessity for fixed chart monitoring.
What’s and Technique of Vary Breakout (RBO)
Definition:Vary Breakout (RBO) technique identifies a horizontal value vary fashioned over a specified time window—usually when the market is quiet or consolidating. The excessive and low inside this vary outline a “field.” Cease orders are positioned simply exterior the field in anticipation of a breakout in both route.
Technique Overview:
Time Window:Outline the beginning and finish time for the vary (e.g., 01:00 to 05:00), and the period of the field is (5 to 7hours). Field Formation:Measure the excessive and low throughout this era. Order Placement:Place Purchase Cease barely above the excessive, and Promote Cease beneath the low. Cease Loss:Primarily based on the field dimension (vary top). Order Expiration:If no breakout happens inside a set period, cancel pending orders. Revenue Exit:By way of trailing cease or time-based shut.
Use Case:Generally used through the Asian session to commerce the London breakout. Best for capturing momentum as soon as value escapes the quiet hours.
Utilizing ICMarkets dealer for instance, the field (help/resistance) is about from 03:00hour to 10:00hour, (10:00 is the beginning of London Session) with cease loss on the different facet of the field and shut positions at 18:30hour.
What’s and Technique of Opening Breakout (OBO)
Definition:Opening Breakout (OBO) technique focuses on capturing the volatility surge that always follows a serious market session open (e.g., London or New York). It defines a brief opening vary, then locations orders exterior that vary to catch the rapid value motion.
Technique Overview:
Opening Time Field:Set a brief interval after market open (5 to 60min). Field Formation:Outline excessive and low of value throughout this time. Breakout Orders:Purchase Cease above the excessive, Promote Cease beneath the low. Cease Loss and Take Revenue:Primarily based on field top or through trailing logic. Cancel Time:Untriggered orders expire after a user-defined time. Exit Choices:Time shut, trailing cease, or mounted revenue ranges.
Use Case:Best for buying and selling the primary burst of motion through the London or New York opening bell. Capitalizes on the surge of liquidity and directional momentum that always follows.
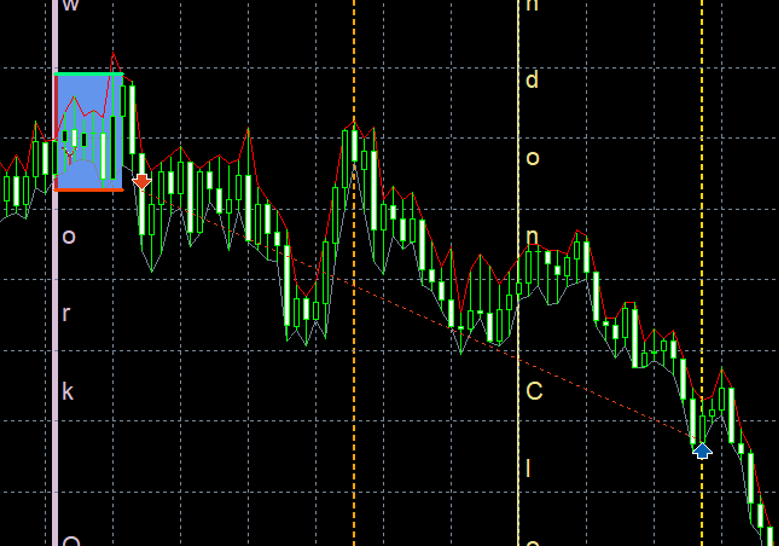
Beginning of field (highest/lowest) is at New York Session (10:00hour) and finish of field is 35 minutes from begin. Use shut by time choice at 18:00hour
Terminology 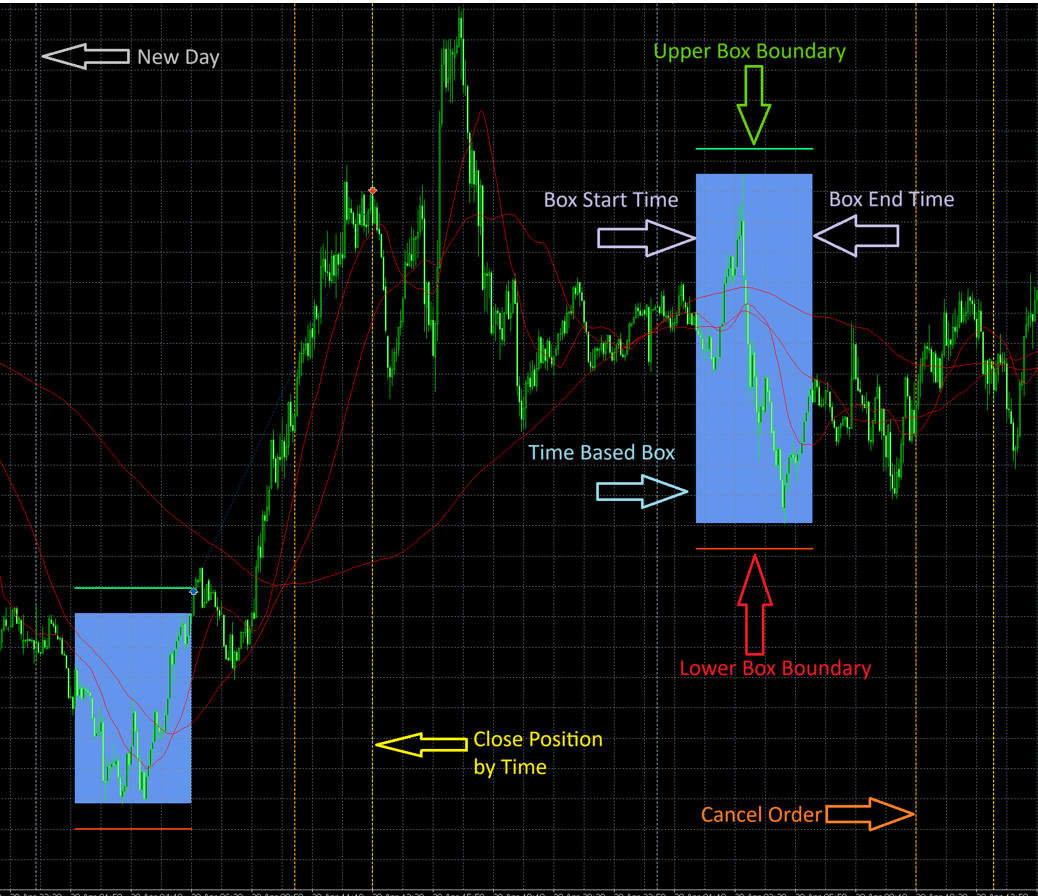
New Day (Gray Arrow)Marks the start of a brand new buying and selling day. The EA resets and begins monitoring the brand new breakout field primarily based on configured begin time.
Field Vary (Blue Rectangle)Represents the outlined Field Time Vary, throughout which the EA measures the best and lowest costs to type the breakout zone. An unfilled field signifies field vary filter doesn’t meet the criterial and thus no orders will likely be positioned for that day.
Higher Field/Commerce Boundary (Inexperienced Arrow)Signifies the higher breakout stage. If value breaks above this level, a Purchase Cease order will likely be triggered (if circumstances permit). That is field stage plus offset.
Decrease Field/Commerce Boundary (Pink Arrow)Signifies the decrease breakout stage. If value breaks beneath this line, a Promote Cease order will likely be triggered (if circumstances permit). That is field stage minus offset.
Cancel Order (Orange Arrow)Happens after a pre-defined Cancel Order Period following the top of Field Time. Any pending Purchase/Promote Cease orders are cancelled if not triggered by this level.
Shut Place by Time (Yellow Arrow)Defines the compelled shut time for any remaining open positions. This happens after the cancel time, and ensures no trades carry ahead into unsure market hours.
Issue and PercentageFactor and Share is all the time with respect to a different setting/parameter/worth. The principle distinction between components and percentages is that components are complete numbers that divide one other quantity precisely, whereas percentages are fractions of 100 that describe proportional relationships.
All-in-One EA might be discovered right here:
Settings
1. Cash Administration
These settings management how the EA manages place sizing and danger.
Cash Administration Kind (MMType)
Mounted Lot Measurement (MMByFixed): Use a set lot dimension for all trades.Instance: MMFixed = 0.2 → Outcome: All trades use 0.20 tons. Fairness Ratio (MMByEquityRatio): Calculate lot dimension primarily based on a ratio of fairness (primarily based on 0.01 lot per $100 fairness).Instance: MMEquityRatio = 100, Fairness = $1,000 → (1000 / 100) × 0.01 = 0.10 tons. Steadiness Ratio (MMByBalanceRatio): Calculate lot dimension primarily based on a ratio of account steadiness. (primarily based on 0.01 lot per $100 fairness).Instance: MMBalanceRatio = 200, Steadiness = $5,000 → (5000 / 200) × 0.01 = 0.25 tons. Danger Share (MMByRiskPC): Calculate lot dimension primarily based on a share of fairness risked per commerce.Instance: MMRiskPC = 2, Fairness = $10,000, SL = 50 factors, 1 level = $1 → $200 / 50 = 4.00 tons. For this setting, the loss is $200 which is 2% of $10000. Repair Greenback Loss (MMByFixedDollar): Calculate lot dimension primarily based on a set greenback quantity risked per commerce. This feature is nice for controlling the quantity of loss.Instance: MMFixedDollar = 125, and the account steadiness is 25000, the loss every time is 0.5%. With the loss quantity mounted, it’s straightforward to manage the drawdown.
2. Field Time
This part defines the particular time window used to attract the breakout field. The EA calculates the excessive and low (or close-to-close) inside this window to find out breakout boundaries. The field might be anchored from both the beginning time or the top time, relying in your buying and selling logic.
This flexibility permits the person to outline the vary both ahead from a identified start line, or backward from a identified ending level, by specifying a period.
Parameters
Field Timeframe (TimeframeRange)Timeframe used to calculate the candles forming the field.Instance: TimeframeRange = PERIOD_M5 → Field makes use of 5-minute candles. Field Kind (BoxType) Excessive/Low (HighLow): Makes use of the best excessive and lowest low inside the field window. Assist/Resistance (HighLowClosed): Makes use of the best shut and lowest shut inside the field window. Field Anchor Time (BoxAnchor)Defines the time reference for calculating the field vary. Vary Begin (RangeStart): The field begins on the specified time, and ends after an outlined period. Vary Finish (RangeEnd): The field ends on the specified time, and its begin is calculated by subtracting the period. Field Begin Time (RangeStartHour, RangeStartMinute, RangeStartSecond)If BoxAnchor = RangeStart, this defines the precise time the field begins.Instance: RangeStart = 02:00:00. Field Finish Time (RangeEndHour, RangeEndMinute, RangeEndSecond)If BoxAnchor = RangeEnd, this defines the precise time the field ends.Instance: RangeEnd = 07:30:00. Field Period (when BoxAnchor = RangeStart or RangeEnd)The second set of time inputs (i.e., RangeEnd or RangeStart) is interpreted because the period.Instance 1: BoxAnchor = RangeStart, Begin = 02:00, Period = 5h30m → Field begins at 02:00 and ends at 07:30.Instance 2: BoxAnchor = RangeEnd, Finish = 07:30, Period = 4h00m → Field begins at 04:30 and ends at 07:30. Randomise Field Time (RandomRange)Permits or disables bounded randomisation of the field window to scale back predictability. Randomised Vary Time (RangeSecondDelta)Most variety of seconds to randomly shift each the beginning and finish instances.Instance: RangeSecondDelta = 180 → Begin and/or finish time could shift by ±180 seconds (3 minutes).
2.1 Field Methodology
This part defines how the field (vary) is calculated utilizing volatility-based indicators corresponding to Common True Vary (ATR) and Common Day by day Vary (ADR).
ATR Timeframe (ATRTF): Timeframe used to calculate the ATR worth (e.g., ATRTF = H1). ATR Interval (ATRPeriod): Variety of candles used to calculate the ATR worth. Instance: ATRPeriod = 14 → ATR is calculated from the final 14 candles of the chosen timeframe. Common ADR Interval (ADRPeriod): Variety of days used to calculate the Common Day by day Vary. Instance: ADRPeriod = 20 → ADR is calculated from the previous 20 each day candles.
2.2 Field Offset
The offset add on or minus to the time primarily based type field to type Higher Field Boundary and Decrease Field Boundary. These are the degrees the trades will likely be positioned
Field Offset Kind (OffsetType)
Offset Off (OffsetOff): No offset. Mounted Level (OffsetByFixedPoint): Offset by a set variety of factors.Instance: OffsetFixedPoint = 20 → Entry value is adjusted by +20 factors.Instance: OffsetFixedPoint = -13 → Entry value is adjusted by -13 factors. Mounted Share (OffsetByFixedPC): Offset by a share of the field dimension.Instance: Field dimension = 100 factors, OffsetFixedPC = 10 → Offset = 10% of 100 = 10 factors.Instance: Field dimension = 100 factors, OffsetFixedPC = -5 → Offset = -5% of 100 = 5 factors. ATR (OffsetByATR): Offset by a share of the ATR.Instance: ATR = 50 factors, OffsetATR = 20 → Offset = 20% of fifty = 10 factors.Instance: ATR = 50 factors, OffsetATR = -10 → Offset = -10% of fifty = 5 factors. ADR (OffsetByADR): Offset by a share of the ADR.Instance: ADR = 120 factors, OffsetADR = 25 → Offset = 25% of 120 = 30 factors.Instance: ADR = 120 factors, OffsetADR = -5 → Offset = -5% of 120 = -6 factors. Value (OffsetByPrice): Offset by a share of the present value.
Random Offset Kind (RandomOffset)
Random Offset Off (RandomOffsetByOff): No random offset. Random by Level (RandomOffsetByPoint): Random offset by mounted factors.Instance: RandomOffsetPoint = 15 → A random quantity between -15 and 15 factors is added to the offset. Random by Share (RandomOffsetByPC): Random offset by share.Instance: Field dimension = 100 factors: RandomOffsetPC = 5 → offset is randomized between -5 and +5 factors. RandomOffsetPC = 10 → offset is randomized between -10 and +10 factors. RandomOffsetPC = 15 → offset is randomized between -15 and +15 factors.
2.3 Field Vary Filter
This filter restricts buying and selling to solely when the breakout field dimension is inside a desired vary. It helps keep away from buying and selling during times of both too little or an excessive amount of volatility, bettering commerce high quality and consistency.
Vary Filter Kind (RangeType)
Off (RangeByOff): No filter utilized. Mounted Level (RangeByFixedPoint): Filter primarily based on a set level vary.Instance: MinRangePoint = 40, MaxRangePoint = 100 → Trades are solely taken if the field dimension is between 40 and 100 factors. ATR (RangeByATR): Filter primarily based on a share of ATR.Instance: ATR = 80 factors, MinRangeATR = 50, MaxRangeATR = 150 → Trades allowed if field dimension is between 40 and 120 factors (50%-150% of ATR). ADR (RangeByADR): Filter primarily based on a share of ADR.Instance: ADR = 120 factors, MinRangeADR = 20, MaxRangeADR = 80 → Field should be between 24 and 96 factors. Value (RangeByPrice): Filter primarily based on a share of value.Instance: Value = 1.3000, MinRangePrice = 0.05, MaxRangePrice = 0.1 → Allowed field dimension: 65 to 130 factors (0.05%-0.1% of value).
3. Cancel Orders
These settings management when pending orders are cancelled, if not triggered by this time.
This defines the period after which pending orders are canceled, measured from the Field Finish Time (not from the Field Begin).
Cancel Order Period (CancelOrdersHour, CancelOrdersMinute, CancelOrdersSecond): Period added to the Field Finish Time after which pending orders are canceled. Randomise Cancel Order (RandomCancelOrder): Allow or disable bounded randomization of cancel order time. Randomised Cancel Time (CancelOrderSecondDelta): Most seconds to randomize the cancel time.
Instance:
RangeStartHour = 2, RangeStartMinute = 0 RangeEndHour = 5, RangeEndMinute = 30→ Field ends at 07:30 CancelOrdersHour = 6, CancelOrdersMinute = 0→ Cancel Time = 07:30 + 6:00 = 13:30 If RandomCancelOrder = true, CancelOrderSecondDelta = 180→ Cancel time could differ between 13:27:00 and 13:33:00
4. Shut Positions
This defines the period after which positions are force-closed, measured from the Cancel Orders Time. That is helpful to keep away from holding trades past particular hours or market periods and shut earlier than the day ends.
Shut Kind (CloseType): CloseByTime: Shut trades strictly on the shut time. ClosebyTP: Shut trades solely when take revenue is hit. CloseByTP_Time: Shut by both take revenue OR compelled shut time, whichever comes first. Shut Positions Period (ClosePositionsHour, ClosePositionsMinute, ClosePositionsSecond): Period after cancel time to shut open trades. Randomise Shut Time (RandomClosePosition): Permits/disables randomisation of place shut time. Shut Time Random Delta (ClosePositionSecondDelta): Max variety of seconds to randomly shift the shut time.
Instance:
Field Finish = 07:30, CancelOrdersHour = 6:00 → Cancel time = 13:30 ClosePositionsHour = 2, ClosePositionsMinute = 0 → Shut time = 13:30 + 2:00 = 15:30 If RandomClosePosition = true, ClosePositionSecondDelta = 180 → Closing shut could occur between 15:27 and 15:33
5. Cease Loss
These settings outline how the cease loss (SL) is calculated for every commerce. You’ll be able to select from varied calculation strategies together with a set variety of factors, range-based components, or dynamic volatility indicators like ATR and ADR.
Cease Loss Kind (SLType):
Field Issue (SLByFactor): Cease loss is about as a a number of (issue) of the field dimension.Instance:
o If field dimension = 100 factors, and SLFactor = 1.5 → SL = 100 × 1.5 = 150 factors
o If field dimension = 100 factors, and SLFactor = 0.5 → SL = 100 × 0.5 = 150 factors, that is good to shut a commerce with smaller cease loss if a breakout isn’t profitable.
Mounted Level (SLByPoint): Cease loss is about as a set variety of factors.Instance: SLPoint = 80 → SL = 80 factors ATR-Primarily based (SLByATR): Cease loss is calculated as a share of the ATR worth.Instance: ATR = 50 factors, SLATR = 120 → SL = 50 × 1.2 = 60 factors ADR-Primarily based (SLByADR): Cease loss is calculated as a share of the ADR worth.Instance: ADR = 100 factors, SLADR = 70 → SL = 100 × 0.7 = 70 factors Value Issue (SLByPrice): Cease loss is calculated as a percentage-based issue of the present value.Instance: Value = 1.10000, SLPrice = 0.1 → SL = 0.1% of value = 1.10000 × 0.001 = 11 factors Off (SLOff): No cease loss will likely be utilized. That is extremely dangerous and never beneficial for many use instances.
Random Cease Loss Kind (RandomSL):
Randomization introduces managed variation to make your SL ranges much less predictable, which might help in prop agency environments or scale back predictability by brokers.
Random SL Off (RandomSLByOff): No randomization is utilized to cease loss. Random by Level (RandomSLByPoint): SL is randomized by a lot of factors above or beneath the bottom SL.Instance: RandomSLPoint = 15 → Closing SL = Base SL ± random worth between -15 and +15 factors Random by Share (RandomSLByPC): SL is randomized by a share issue of the bottom SL.Examples: RandomSLPC = 5 → SL fluctuates inside ±5% vary of base SL RandomSLPC = 10 → ±10% vary RandomSLPC = 15 → ±15% rangeIf base SL = 100 factors and RandomSLPC = 10 → SL will differ between 90 and 110 factors
6. Take Revenue
These settings management how the Take Revenue (TP) stage is calculated for every commerce. You’ll be able to outline TP primarily based on a set distance, or dynamically utilizing indicators like ATR, ADR, or present value ranges. TP placement is essential for controlling reward-to-risk ratios and exit habits.
Take Revenue Kind (TPType):
Cease Loss Issue (TPByFactor): TP is about as a a number of of the cease loss. That is the setting for conventional risk-to-reward ratio.Instance: If SL = 80 factors, and TPFactor = 2 → TP = 80 × 2 = 160 factors, a RRR of two. Mounted Level (TPByPoint): TP is about at a set variety of factors from the entry.Instance: TPPoint = 100 → TP = 100 factors ATR-Primarily based (TPByATR): TP is calculated as a share of the ATR worth.Instance: ATR = 60 factors, TPATR = 150 → TP = 60 × 1.5 = 90 factors ADR-Primarily based (TPByADR): TP is calculated as a share of the ADR worth.Instance: ADR = 120 factors, TPADR = 80 → TP = 120 × 0.8 = 96 factors Value Issue (TPByPrice): TP relies on a share of the present market value.Instance: Value = 1.10000, TPPrice = 0.15 → TP = 1.10000 × 0.0015 = 16.5 factors Off (TPOff): No Take Revenue stage will likely be utilized. Trades can shut solely by cease loss or handbook intervention.
Random Take Revenue Kind (RandomTP):
To extend commerce robustness and scale back system predictability, TP ranges might be barely different round their calculated worth.
Random TP Off (RandomTPByOff): No randomization is utilized to Take Revenue. Random by Level (RandomTPByPoint): Randomize TP stage by a lot of factors.Instance: RandomTPPoint = 20 → TP = Base TP ± random quantity from -20 to +20 factors Random by Share (RandomTPByPC****): Randomize TP stage by a share of the bottom TP.Examples: RandomTPPC = 5 → TP varies inside ±5% of calculated worth RandomTPPC = 10 → ±10% vary RandomTPPC = 15 → ±15% rangeIf base TP = 100 factors and RandomTPPC = 10 → TP will differ between 90 and 110 factors
7. Trailing Cease
This part defines how the EA adjusts the Cease Loss (SL) as the value strikes in your favor. Trailing Stops assist lock in earnings whereas maintaining positions open throughout beneficial developments. You’ll be able to select from completely different trailing strategies and optionally randomize them to scale back system predictability.
Trailing Cease Swap (Trailing_Stop_Switch)
Permits or disables trailing cease performance.
Trailing Cease Kind (TSType)
By Cease Loss Share (TSBySL): Trailing Cease is calculated as a share of the unique SL.Instance: If SL = 100 factors, TSSL = 33.33 → Trailing Cease = 33.33 factors Mounted Level (TSByFixedPoint): Trailing Cease is about to a set variety of factors.Instance: TSPoint = 333 → Trailing Cease = 333 factors ATR-Primarily based (TSByATR): Trailing Cease relies on a share of the ATR worth.Instance: ATR = 60 factors, TSATR = 5 → Trailing Cease = 60 × 0.05 = 3 factors ADR-Primarily based (TSByADR): Trailing Cease relies on a share of the ADR.Instance: ADR = 150 factors, TSADR = 1 → Trailing Cease = 150 × 0.01 = 1.5 factors Value Share (TSByPrice): Trailing Cease is calculated as a share of the present value.Instance: Value = 1.20000, TSPrice = 0.1 → Trailing Cease = 1.20000 × 0.001 = 12 factors
Path Level Share (Path)
Defines how a lot of the calculated Trailing Cease is used because the set off to maneuver SL.Instance:
If TSPoint = 333 and Path = 50 → SL trails when value strikes by 333 × 0.5 = 166.5 factors
Path Above Break-Even Swap (Trail_Above_Switch)
Permits or disables further management that triggers trailing solely when the value goes additional above breakeven.
Path Above Issue (Trail_Above)
Defines how far the value should transfer past breakeven earlier than the trailing logic begins.Instance: Trail_Above = 0.25 and TSPoint = 333 → Path begins after 333 × 0.25 = 83.25 factors above breakeven
Random Trailing Cease Kind (RandomTS)
Randomization helps add variability to trailing cease ranges to scale back the prospect of system exploitation or overfitting.
Random Off (RandomTSByOff): No random variation utilized to trailing cease. Random by Level (RandomTSByPoint): Provides or subtracts random factors from trailing cease.Instance: RandomTSPoint = 5 → Trailing Cease could differ between ±5 factors Random by Share (RandomTSByPC): Applies random variation as a share.Examples: RandomTSPC = 5 → ±5% of base trailing cease RandomTSPC = 10 → ±10% RandomTSPC = 15 → ±15%
8. Trades
These settings management commerce habits.
Cancel Reverse Order (COO_Switch): Cancel reverse pending orders when a commerce is opened.
Purchase and/or Promote Trades (BorS):
Purchase and Promote (BuyandSell): Permit each purchase and promote trades. Purchase Solely (BuyOnly): Permit solely purchase trades. Promote Solely (SellOnly): Permit solely promote trades. Purchase and Promote Off (BuyandSellOff): Disable buying and selling completely.
Max Lengthy Trades (MaxLongTrades):Defines the utmost variety of purchase trades per day.Instance: MaxLongTrades = 2 → Solely two purchase orders might be positioned per day.
Max Brief Trades (MaxShortTrades):Defines the utmost variety of promote trades per day.Instance: MaxShortTrades = 3 → As much as three promote orders might be positioned per day.
Max Complete Trades (MaxTotalTrades):Defines the utmost whole variety of trades per day (purchase + promote).Instance: MaxTotalTrades = 5 → A most of 5 trades (mixed purchase and promote) will likely be executed in a single day.
9. Day to Commerce
These settings management which days of the week the EA is allowed to put trades. You’ll be able to selectively allow or disable buying and selling for every day.
Commerce Monday (TradeMonday):true – EA will open trades on Mondays.false – EA is not going to open trades on Mondays. Commerce Tuesday (TradeTuesday):true – EA will open trades on Tuesdays.false – EA is not going to open trades on Tuesdays. Commerce Wednesday (TradeWednesday):true – EA will open trades on Wednesdays.false – EA is not going to open trades on Wednesdays. Commerce Thursday (TradeThursday):true – EA will open trades on Thursdays.false – EA is not going to open trades on Thursdays. Commerce Friday (TradeFriday):true – EA will open trades on Fridays.false – EA is not going to open trades on Fridays. Commerce Saturday (TradeSaturday):true – EA will open trades on Saturdays (hardly ever used except buying and selling crypto).false – EA is not going to open trades on Saturdays. Commerce Sunday (TradeSunday):true – EA will open trades on Sundays (hardly ever used except buying and selling crypto).false – EA is not going to open trades on Sundays.
10. Confluence
These settings add further filters for commerce entry, enabling stronger affirmation primarily based on development and volatility confluence. Use of confluence on some devices, can enhance winrate and drawdown.
3 Shifting Averages Filter
Allow 3 MA Filter (CMASwitch): Allow or disable utilizing three transferring averages for development affirmation. MA Timeframe (MAATF): Timeframe used for calculating the transferring averages (e.g., PERIOD_H1). MA Methodology (MAMethod): The tactic used for calculating the transferring common (e.g., SMA, EMA). Quick MA Interval (CMA1Period): Interval for the fast paced common. Medium MA Interval (CMA2Period): Interval for the medium transferring common. Sluggish MA Interval (CMA3Period): Interval for the gradual transferring common.
Instance: If CMA1 = 21, CMA2 = 50, CMA3 = 200, then:
Entry allowed provided that: MA21 > MA50 > MA200 (uptrend), or MA21 < MA50 < MA200 (downtrend).
ADI (Common Directional Index) Filter
Allow ADI Filter (CADISwitch): Allow or disable the ADI confluence filter. ADI Timeframe (CADITF): Timeframe used for calculating ADX. ADI Interval (CADIPeriod): Interval used for ADX calculation. ADX Threshold (CADIMainLevel): Minimal required ADX worth for development affirmation. Minimal DI+ / DI− Degree (CADILevel): Required minimal energy of DI+ vs DI− for Purchase/Promote alerts. DI+ confirms Purchase and DI− confirms Promote. DI Issue (CADIDiff****): Minimal distinction between DI+ and DI− to substantiate directional development.
Logic:
Purchase Sign = DI+ > DI− × CADIDiff AND DI+ > CADILevel AND ADX > CADIMainLevel Promote Sign = DI− > DI+ × CADIDiff AND DI− > CADILevel AND ADX > CADIMainLevel
Examples (assuming CADILevel = 40, CADIDiff = 3):
DI+ = 46, DI− = 15, ADX = 42→ This setup produces a Purchase sign as a result of:46 > 15×3 = 45, 46 > 40, and ADX = 42 > 30 DI+ = 12, DI− = 43, ADX = 38→ This setup produces a Promote sign as a result of:43 > 12×3 = 36, 43 > 40, and ADX = 38 > 30 DI+ = 36, DI− = 11, ADX = 35→ No entry sign as a result of:Though 36 > 11×3 = 33, the DI+ worth 36 isn’t better than the edge CADILevel = 40
ADR Filter
Allow ADR Filter (CADRSwitch): Permits or disables filtering primarily based on the Common Day by day Vary (ADR). ADR Timeframe (CADRTF): The timeframe used to calculate ADR (e.g., PERIOD_D1). ADR Interval (CADRPeriod): The variety of days over which the ADR is averaged. Minimal ADR Degree (CADRLevelMin): The minimal ADR worth required for a commerce to be legitimate. Most ADR Degree (CADRLevelMax): The utmost ADR worth allowed for a commerce to be legitimate.
Goal:This filter ensures trades are solely taken when the present market volatility (as measured by ADR) is inside an outlined vary. It avoids alerts throughout overly quiet or excessively risky market circumstances.
Instance:
CADRPeriod = 14, CADRLevelMin = 50, CADRLevelMax = 150 The EA calculates the typical of the final 14 each day candle ranges and determines it’s 85 factors. Commerce is allowed as a result of 85 is inside the 50–150 level vary. If ADR = 40 → commerce is skipped (inadequate volatility). If ADR = 200 → commerce is skipped (volatility exceeds the higher threshold, presumably as a result of information or irregular market circumstances).
Bollinger Bands Confluence
Allow Bollinger Bands Filter (CBBSwitch): Permits or disables using Bollinger Bands as a confluence filter. Bollinger Bands Timeframe (CBBRTF): Timeframe used for calculating the Bollinger Bands (e.g., PERIOD_D1). Bands Interval (CBBPeriod): Variety of durations used to calculate the bands. Customary Deviation (CBBDev): Deviation multiplier for higher and decrease bands. Minimal Band Vary (CBBLevelMin): Minimal allowed vary between higher and decrease Bollinger Bands (used as a volatility filter). Most Band Vary (CBBLevelMax): Most allowed vary between bands (used to exclude overly risky circumstances).
How It Works:
This filter measures the distance between the higher and decrease bands on the chosen timeframe. If the band width falls inside the specified min/max thresholds, then the breakout sign is taken into account legitimate.
Instance:
CBBPeriod = 20, CBBDev = 2.0, CBBLevelMin = 30, CBBLevelMax = 120 If Bollinger Band width = 85 pips → passes the filter If Bollinger Band width = 15 pips or 150 pips → filtered out
This ensures breakouts are solely thought-about when volatility is inside a wholesome vary — not too compressed (low volatility) or too expanded (excessive danger of mean-reversion).
The above indicator might be present in MT4/MT5 Terminal. To raised perceive how the above customary indicators perform, you possibly can add them on to your chart in MT4 or MT5. This lets you visually observe how the EA’s confluence logic interacts with Shifting Averages, ADX, Bollinger Bands and ADR in actual time on your to formulate your individual setting.
11. Common Settings
These settings management the overall habits and logging of the EA.
Magic Quantity (MagicNumber):Distinctive identifier assigned to the EA’s trades. This ensures the EA solely manages its personal trades and avoids conflicts with different EAs.Instance: MagicNumber = 1970 → All trades from this EA will carry this magic quantity. EA Remark (EaOrderComment):A customized remark connected to every order positioned by the EA. This might help in figuring out trades within the terminal or throughout journal/debug evaluation.Instance: EaOrderComment = “AIO Breakout” → All trades will embody this remark. Chart Remark Swap (ChartComment):true – The EA shows dynamic commerce or strategy-related feedback on the chart.false – Disables chart feedback. Debug Message Swap (DebugSwitch):true – Permits detailed logs within the Consultants and Journal tabs for debugging or evaluation.false – Disables additional debug messages to scale back litter.
12. Visible Settings
These settings management how the EA seems on the chart throughout buying and selling or backtesting. Use these settings to reinforce the visibility and readability of chart annotations. This built-in indicator doesn’t have an effect on the field/vary setting.
Field Coloration (RangeColor): Defines the visible shade of the principle vary field. Observe that if Field Vary Filter is activate and the field vary/dimension doesn’t meet the filter standards, the field seems as boadered, not stuffed. Cease Trades Coloration (StopColor): The colour of the horizontal line that reveals the place trades cease. Cancel Pending Coloration (CancelColor): The colour used to show the cancel pending orders line. Day Open Coloration (DayOpenColor): The road shade marking the day’s open value. Higher Field Coloration (UpperBoxColor): Coloration of the higher line of the breakout field. Decrease Field Coloration (LowerBoxColor): Coloration of the decrease line of the breakout field. Present Information (ShowInfo): Present or disguise the EA’s standing and particulars on the chart. Textual content Measurement (TextSize): Units the dimensions of the displayed font on the chart. Textual content Coloration (TextColor): Defines the font shade of displayed data. Field Coloration (BoxColor): Background shade of the knowledge field.
13. Commerce Classes IndicatorThese settings permit the EA to show visible markers on the chart that point out the beginning of key buying and selling periods. This helps merchants acknowledge optimum breakout home windows and durations of low or excessive volatility primarily based on session timing.
• Allow Commerce Classes Indicator (TradeSessionsIndicatorSwitch): Activates or off the show of buying and selling session markers. If enabled (true), session labels will seem on the chart.• Tokyo Session Begin Hour (JP_Start_Hour): Units the beginning time (hour) for the Tokyo session, usually related to decrease volatility and generally used to type the breakout vary (RBO technique).• London Session Begin Hour (LD_Start_Hour): Units the hour when the London buying and selling session begins. It is a widespread opening level for breakout alternatives, particularly in OBO.
• New York Session Begin Hour (NY_Start_Hour): Units the hour of the New York session begin. It’s usually linked to excessive volatility and overlaps with London.• Textual content Spacing (Spacing): Adjusts the vertical spacing between session label texts. Helpful for maintaining chart show clear and readable when a number of periods are proven.
Thick line denotes beginning of a session and skinny line denotes ending of a session.Settings for brokers with server timezone in GMT+2/3, for instance ICMarkets is:Tokyo Buying and selling Session Beginning Hour = 2London Buying and selling Session Beginning Hour = 10New York Buying and selling Session Beginning Hour = 15
Some brokers are utilizing UTC as buying and selling server timezone and a few might be others. You need to discover out your dealer server timezone and set the mandatory above values.
14. Backtest
These settings management the habits of backtests. Use these choices to hurry up checks or scale back execution time whereas sustaining logical habits.
Quick Backtest (FastBacktest): T-Kind: Use T-type quick backtesting logic. S-Kind: Use S-type quick backtesting logic. Quick Backtest Off: Disable quick backtest optimizations. T-type Interval (TInt): Specifies the interval between check occasions throughout T-type testing, from 3 and above. Greater variety of this produce quicker backtest even with each actual ticks.



