Lambert right here: Ah, “Correct info.”
By Daron Acemoglu, Institute Professor within the Division of Economics at Massachusetts Institute of Expertise (MIT), Cevat Giray Aksoy, Affiliate Director of Analysis within the Workplace of the Chief Economist at European Financial institution for Reconstruction and Growth (EBRD), Affiliate Professor of Economics at King’s School London, Ceren Baysan, Assistant Professor of Economics at College Of Toronto, Carlos Molina, Analysis Assistant Professor at College Of South Carolina, and Gamze Zeki. Initially printed at VoxEU.
Authoritarian regimes typically keep energy through cultivating misperceptions concerning the high quality of state establishments and the worth of democracy. This leads residents to underestimate the deterioration of democratic establishments, affecting their voting behaviour. This column presents findings from a examine of voters in the course of the Might 2023 Turkish presidential elections. Offering correct info considerably elevated assist for opposition events by swaying voters who initially underestimated the deterioration of institutional high quality and had been leaning in direction of the incumbent alliance. Addressing misperceptions might result in higher public demand for democracy, suggesting that correct info campaigns may assist problem authoritarian narratives.
The Experiments
We use a web-based experiment and a large-scale discipline experiment involving 880,000 voters. In each, we offer correct (research-based) info on the state and implications of democracy and media freedom for mitigating the affect of pure disasters and corruption ranges. This info was primarily based on the evolution of Turkish establishments primarily based on V-DEM knowledge and from related analysis on the connection between democracy and pure disasters (e.g. Besley and Burgess 2002, Cao 2024, Kahn 2005) and media freedom and corruption (e.g. Brunetti and Weder 2003, Ferraz and Finan 2008, Larreguy et al. 2020). These points had been particularly salient for Turkish voters following the devastating February 2023 earthquake, which claimed over 50,000 lives and displaced greater than 1,000,000 individuals. The catastrophe was worsened by unsafe constructing practices enabled by native and nationwide corruption (Acemoglu and Tokgoz 2023).
Within the discipline experiment, we applied two variations of the informational remedy by randomised door-to-door canvassing on the neighbourhood stage. This design allowed us to mix the experimental variation with high-quality administrative and electoral knowledge (as in Baysan 2022). The research-based informational remedy offered purely factual info, explaining that declines in media independence improve corruption. The fundamental informational remedy conveyed info in easier phrases and included extra evocative language on democracy, transparency, and corruption.1
Within the on-line experiment, we included a placebo remedy, as in Acemoglu et al. (2020), which supplied encouragement with out delivering any substantive info to regulate for potential experimenter demand results. We then examined how the research-based informational therapies on media/corruption and democracy/pure disasters influenced voters’ beliefs about democracy and voting intentions relative to the respective placebo therapies.
Voters’ Baseline Views
The survey part in our on-line experiment permits us to measure the baseline views of supporters from totally different events concerning their assist for democratic establishments, which helps interpret our experimental outcomes. We summarise these findings by specializing in voters from the three important blocs represented in parliament. The incumbent alliance, known as the Individuals’s Alliance, included two of the primary events, AKP and MHP, and is proven in yellow in Determine 1. The opposition alliance, the Nation Alliance, consists of, most significantly, CHP and İYİ Get together, and is proven in darkish blue. The Individuals’s Democratic Get together (HDP) is proven in gray.
Panel A of Determine 1 exhibits that members who voted for the governing coalition in 2018 are considerably extra prone to report that autocracy is typically preferable to democracy than those that supported the opposite two coalitions or didn’t vote in 2018. Panel B presents abstract statistics on voters’ perceptions of how media independence has advanced in Türkiye between 2000 and 2022 (the patterns for “democracy” are comparable). In response to the V-DEM dataset, the precise change is represented by the dashed line. A transparent sample emerges: supporters of the governing coalition have a way more beneficial opinion of how media independence has advanced. Whereas these views might partly mirror partisan bias and motivated reasoning, our on-line experiment is designed to isolate the function of misperceptions. Panel C suggests why there could also be totally different views concerning the high quality of media independence in Türkiye. Individuals’s Alliance supporters had been, if something, extra pessimistic about institutional high quality in comparison with the opposition in 2000, earlier than Erdoğan got here to energy. As Erdoğan’s early reforms expanded non secular rights (in addition to minority rights, anti-corruption efforts, and EU membership), this might have disproportionately benefited these supporters and formed their views on institutional evolution over time, probably driving each their assist and misperceptions.
Determine 1 Baseline institutional views by political affiliation
Word: This determine presents the baseline views of members within the on-line experiment primarily based on political affiliation (Individuals’s Alliance, Nation Alliance, and HDP supporters). Affiliations are primarily based on self-reported votes within the 2018 election. Panels A and B present the extent to which respondents assist authoritarian governments and their perceptions about how media advanced between 2000 and 2023, respectively. The dashed line in Panel B signifies the precise change from the V-DEM knowledge set. Panel C shows voters’ perceptions of democratic establishments in Türkiye in 2000. The bars signify imply scores for every political affiliation. The whiskers present 95 p.c confidence intervals.
Predominant Outcomes from the On-line Experiment
We report the experimental estimates of the informational therapies on voter beliefs. The primary outcomes are offered in Panel A of Determine 2. The left panel of Panel A is for the valuation of establishments, which measures the extent to which people imagine that democratic establishments are necessary for attaining higher outcomes, whereas the precise panel is for the state of establishments which measures perceptions of how democratic establishments have advanced between 2000 and 2023 in Türkiye. Each variables are in normal deviation items.
Determine 2 Remedy results on beliefs and voting outcomes within the on-line experiment
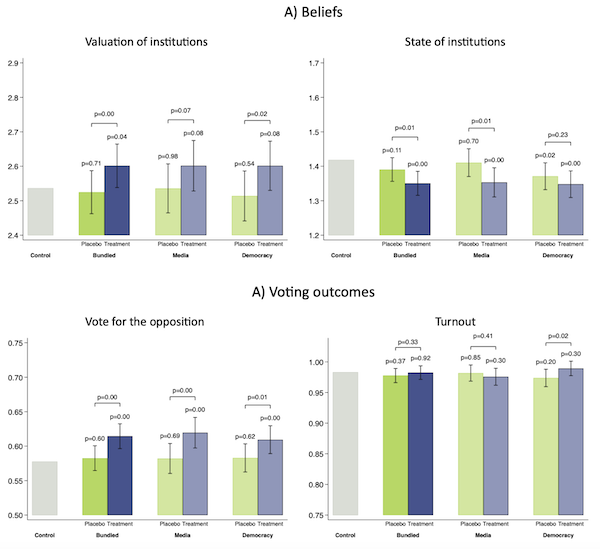
Word: This determine summarises the primary outcomes from the web experiment. It presents estimates of the informational therapies on voter beliefs in Panel A and self-reported voting intentions in Panel B. Valuation of Establishments measures the extent to which people imagine that democratic establishments are necessary for attaining higher outcomes, and State of Establishments measures perceptions of how democratic establishments have advanced between 2000 and 2023 in Türkiye. Each variables are in normal deviation items. Vote for the Opposition and Turnout are dummy variables for voter intentions. The distinction between the heights of the bars for remedy and management teams provides our baseline estimates of the impact of the informational therapies. The whiskers present 95% confidence intervals, whereas the p-values on high of the bars are for these variations being statistically totally different from zero. The p-values on the very high are for the informational remedy being statistically totally different from the placebo.
We see that informational therapies led to a big change within the respondents’ beliefs, offering proof concerning the significance of misperceptions. Pooling the impact of the democracy and media remedy (the bundled remedy), there’s a distinction of 6.5% of an ordinary deviation within the valuation of establishments between the informational remedy and the management teams; this distinction is statistically vital at 4%. There isn’t any distinction between the management group and the placebo remedy. Furthermore, we are able to comfortably reject that the informational and the placebo remedy results are equal. After we separate the media and the democracy therapies, the sample is analogous.
The distinction between the informational remedy group and the management group concerning institutional valuation is quantitatively sizable, equal to roughly half (58%) of the distinction between people in our management group who reached tertiary schooling and people who didn’t.
On the precise, we see a really comparable sample. The informational remedy results in a decline of 6.8% of 1 normal deviation in perceived beliefs about how the state of establishments has modified since 2000. The outcomes are additionally comparable after we separate the media and democracy therapies.
Panel B exhibits the affect of the informational and placebo therapies on the self-reported voting intentions. The bundled remedy will increase the likelihood of voting for the opposition by 3.7 proportion factors relative to the management group. The placebo remedy has a minimal and statistically insignificant coefficient, and the hole between the informational and the placebo therapies is substantial, at 3.2 proportion factors. The informational remedy results are statistically vital at lower than 1%, and so is the distinction between the informational and placebo therapies, as proven in Panel B of Determine 2. We don’t discover vital results on self-reported turnout intentions.
Predominant Outcomes from the Discipline Experiment
The patterns from our discipline experiment, proven in Determine 3, are very clear. Analogously with our on-line experiment outcomes, the informational remedy has a statistically vital and quantitatively substantive impact on opposition vote shares. The bundled remedy will increase the opposition’s vote share within the first-round presidential election by 2.4 proportion factors (equal to a 4.4% improve relative to the management imply). The outcomes, each quantitatively and statistically, are very comparable within the second-round presidential election and within the parliamentary election. Panel B exhibits no affect on voter turnout, which is analogous to the outcomes of voting intention within the on-line experiment. This suggests that the vote share ends in Panel A are usually not pushed by mobilising the opposition however by altering incumbent supporters’ minds. Panel C exhibits a statistically vital constructive impact on the opposition’s vote share within the 2024 municipal elections, virtually a yr after our experiment. This raises the chance that correct info might have swayed some voters sufficiently to change their long-term allegiances and voting patterns.
Determine 3 Remedy results on voting outcomes within the discipline experiment
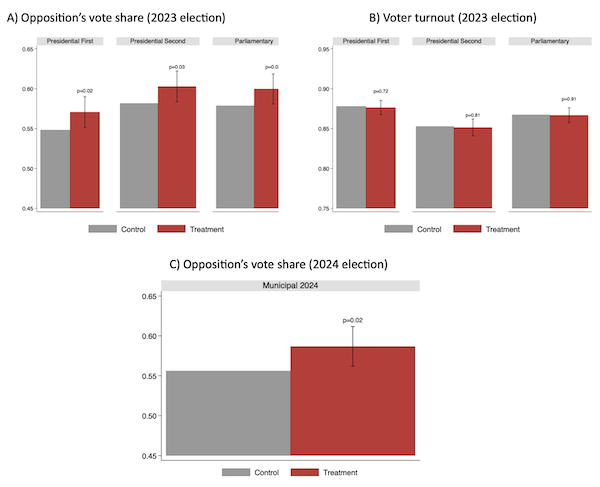
Word: This determine summarises the primary outcomes from the sphere experiment. It presents poll box-level estimates of the remedy results on the opposition’s vote share and turnout within the 2023 first and second spherical presidential, and parliamentary elections in Panels A and B, and the opposition’s vote share within the 2024 municipal election in Panel C. On this determine, we concentrate on the bundled remedy, a dummy variable for the research-based informational or the essential informational remedy on the neighbourhood stage. The distinction between the heights of the bars for remedy and management teams provides our baseline estimates of the impact of the informational therapies. We embody the variety of registered voters at every poll field in 2023, ballot-box geographic controls (inhabitants density, precipitation, temperature, ruggedness, distance to Istanbul, and distance to the coast), neighbourhood-level controls from the 2018 election (opposition’s vote share, turnout, and variety of registered voters), in addition to dummies for various areas and strata mounted results. The whiskers present 95% confidence intervals, whereas the p-values on high of the bars are for these variations being statistically totally different from zero. Normal errors are clustered on the neighbourhood stage.
Mechanisms
Our important outcomes look like pushed by members and voters who initially underestimated the deterioration of institutional high quality and had been leaning in direction of the incumbent alliance. Within the on-line experiment, we discover that members with extra misperceived beliefs modify their perceptions of democratic establishments after receiving correct info and usually tend to shift their voting intentions towards the opposition. In distinction, the placebo remedy exhibits no vital impact on these outcomes.
Within the discipline experiment, neighbourhoods with decrease opposition vote shares within the 2018 parliamentary election – traditionally supportive of the governing coalition – present a lot bigger results from the informational remedy throughout all three 2023 elections. In distinction, neighbourhoods with increased 2018 opposition vote shares present smaller and statistically insignificant results.
These outcomes result in two key factors. First, a considerable portion of presidency supporters view the informational therapies as credible. Second, the therapies have a higher affect on these with extra misperceptions concerning the state of democratic establishments in Türkiye or their effectiveness in delivering desired outcomes.
Conclusion
Authoritarian regimes that stay in energy for prolonged durations can diminish public demand for democracy and media freedom.
Our findings supply a constructive interpretation towards this concern: not less than a part of the assist for authoritarian regimes is coming from misperceptions about their establishments and insurance policies reasonably than a scarcity of precise demand for democracy, and could also be extra malleable than usually presumed. In contrast to in different research (e.g. Adena et al. 2015, Enikolopov et al. 2023, Peisakhin and Rozenas 2018) the place new details about a celebration’s efficiency can deepen polarisation, together with in the same context as ours (Baysan 2022), we don’t observe this impact in both the web or discipline experiments. The truth that our therapies had been primarily based on factual and research-based info designed to right misperceptions and had been, to the extent attainable, offered in a non–partisan method might have been necessary in speaking with authorities supporters and with individuals with totally different baseline beliefs. This implies that such interventions, primarily based on neutral, correct info, have the potential to interrupt self-fulfilling traps the place authoritarian governments persuade their voters that democracy shouldn’t be for them.
References out there on the authentic.




